
ECODEG activity description
- Test the bactericidal response of the product
- Study the aggression capacity of the product against the heads of similar cells, in terms of
- Evaluate the direct action against the ANN of COVID-19
At the same time, he wanted to avoid dilution effects that could give false positive results by wrongly considering the product effective, since the reduction was in fact due only to dilution effects of the sample.
Below are the results of the experiments carried out:
A) – Growth test on untreated soil (identification of optimal concentrations of work – extract from total tests carried out)
- 500 μl bacterial culture medium (E.coli resistant to Ampicillin) + 500 μl STERILE WATER
- 1000 μl mix solution left to act for 3 minutes.
- Collected 1 μl of mixed solution and mix with 499 μl of bacterial culture medium (LB) and sown on Petri dishes with antibiotic (LB + Amp)
- Bacterial Counting (38)

Fig. 1 – Plate with 1 ul of mix solution added – a good reading is noticeable
B)
- 500 μl bacterial culture medium (E.coli resistant to Ampicillin) + 500 μl STERILE WATER
- 1000 μl mix solution left to act for 3 minutes.
-
- Collected 10 μl of mixed solution and mix with 490 μl of culture medium for bacteria (LB) and sown on Petri dishes with antibiotic (LB + Amp)
- Bacterial counting (338)
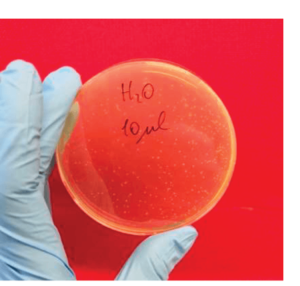
Fig. 2 – Plate with addition of 10 ul of mix solution – you can still notice a good reading
After the first 2 tests the experiment was tested with 100ul obtaining an overpopulation of the plate that becomes illegible.
It was therefore decided to use 10ul of solution in order to have a good reading and a reduced dilution effect.
C)
- 500 μl bacterial culture medium (E.coli resistant to Ampicillin) + 500 μl 50% SOLUTION
- 1000 μl mix solution left to act for 3 minutes.
- Collected 10 μl of mixed solution and mix with 490 μl of culture medium for bacteria (LB) and sown on Petri dishes with antibiotic (LB + Amp)
- Bacterial counting (0)

Fig. 3 – Plate with addition of 10 ul of product as is – Bacterial charge equal to 0
D)
- 500 μl bacterial culture medium (E.coli resistant to Ampicillin) + 500 μl 100% SOLUTION
- 1000 μl mix solution left to act for 3 minutes.
- Collected 10 μl of mixed solution and mix with 490 μl of culture medium for bacteria (LB) and sown on Petri dishes with antibiotic (LB + Amp)
- Bacterial countinga (0)

Fig. 4 – Plate with addition of 10 ul of product at 50% – Bacterial charge equal to 0
BACTERICIDAL ACTIVITY CONCLUSIONS:
On the basis of the resulting evidence, it can be concluded that the product has clear bactericidal activities.
The use even in diluted solutions does not make the product lose effectiveness.
At the same time, it is necessary to evaluate the response curves to bactericidal action in order to define a correct dosage that guarantees full effectiveness.
ECODEG activities on COVID-19
Having clarified the bactericidal activity, the effectiveness of the product against viruses and in particular COVID-19 has been verified.
There are two parallel components to the antiviral action:
1. the product’s ability to attack the viral RNA and degrade it
2. The product’s ability to attack the outer membrane of the capsid (the external structure of the virus that contains and protects viral RNA)
The reason for this check is closely related to the way the virus acts.
The capsid contains the protein groups that allow the virus to attack the host cells and allow the RNA to penetrate the host cell. The degradation of the capsid puts to one the viral RNA that can degrade and that, above all, no longer has the possibility to have the “access keys” to penetrate the host cell.
At the same time the viral RNA tends to degrade in quite a long time. A direct action on the RNA of the virus allows to evaluate the effectiveness of the product at the level of the complete capsid nucleus, thus highlighting a degenerative action also against the viral RNA, effectively destroying the virus in any form it is present (intact or with compromised capsid).
Testing the effectiveness of the product against viral RNA
Three aliquots, each containing 200 ng total RNA, were taken from the total RNA extracted from swab of a patient with COVID-19 in a final volume of 50 μl.
Then, an equal volume of distilled water, ECODEG 50% and ECODEG 100% respectively, was added for a total volume of 100 μl.
The three solutions were incubated at 37°C for 24 hours.
After incubation, using the commercial kit, the three samples were purified and the RNA eluted in 25 μl of distilled water.
Therefore, starting from the RNA obtained from each experimental condition and from equal volumes, the cDNA has been synthesized. To evaluate the integrity of the extracted RNA, the cDNA thus obtained were analyzed in triplicate in real-time PCR, using the QuantStudio3 (Applied Biosystems) tool. The analysis was performed using primer pairs specific for SARS-CoV-2 transcript specific primers (as indicated by the Atlanta CDCs and previously validated by us) through SybrGreen chemistry.
The final analysis of the real-time PCR data showed that in the presence of the ECODEG detergent a decrease in the presence of the viral genome SARS-CoV-2, detectable by molecular investigation, of about 1,000 times, indicative of its evident degradation, was observed.
Testing the effectiveness of the product against the lipid membrane
In order to evaluate the ability of the solution of interest to degrade the lipid membrane, tests were carried out on human-derived cell lines grown on Petri dishes in adhesion to which the culture medium was replaced with 50% and 100% ECODEG detergent solution.
Specifically, 1:1 diluted detergent solution with saline was added to the cells and they were observed under the microscope.
As shown in the photos, after only 30 seconds after the addition of the cleaning solutions, a total lysis of the lipid membrane is observed.
ECODEG detergent solution 50% diluted 1:1 with a saline solution:
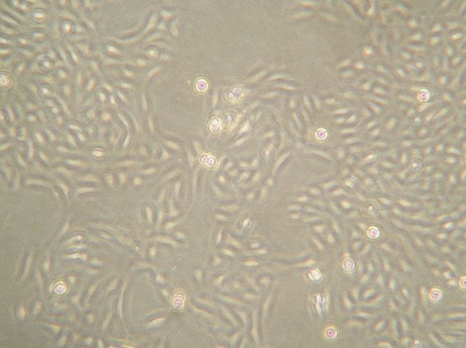
Cells in a saline solution after 30 seconds
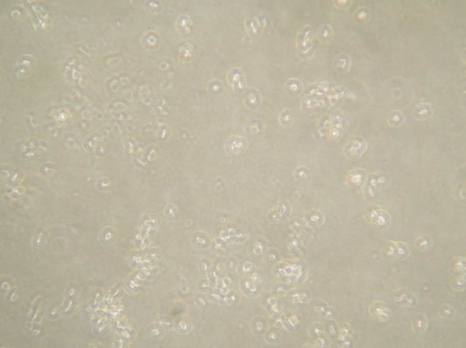
Cells in detergent solution after 30 seconds
ECODEG 100% detergent solution diluted 1:1 with a saline solution:
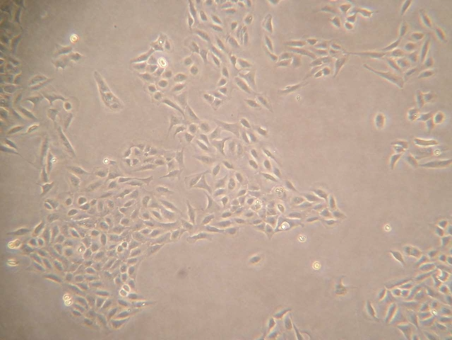
Cells in a saline solution after 30 seconds

Cells in detergent solution after 30 seconds
ANTIVIRAL ACTIVITY CONCLUSIONS:
As it is clear from the tests carried out, the product is effective in both attacking the capsides of the virus by clearly showing direct action against cell membranes.
At the same time the results obtained on the RNA tests show that the same viral RNA has been affected and degraded.
It can therefore be concluded that the product has explicit antiviral activities and is effective in the degradation and inactivation of COVID-19.
As already mentioned in the conclusions concerning the microbiological part, the correct dosage must be verified and guaranteed in order to maintain the efficacy highlighted under the conditions of use.
